Thyroid Health: The Role of MRI in Precise Diagnostics
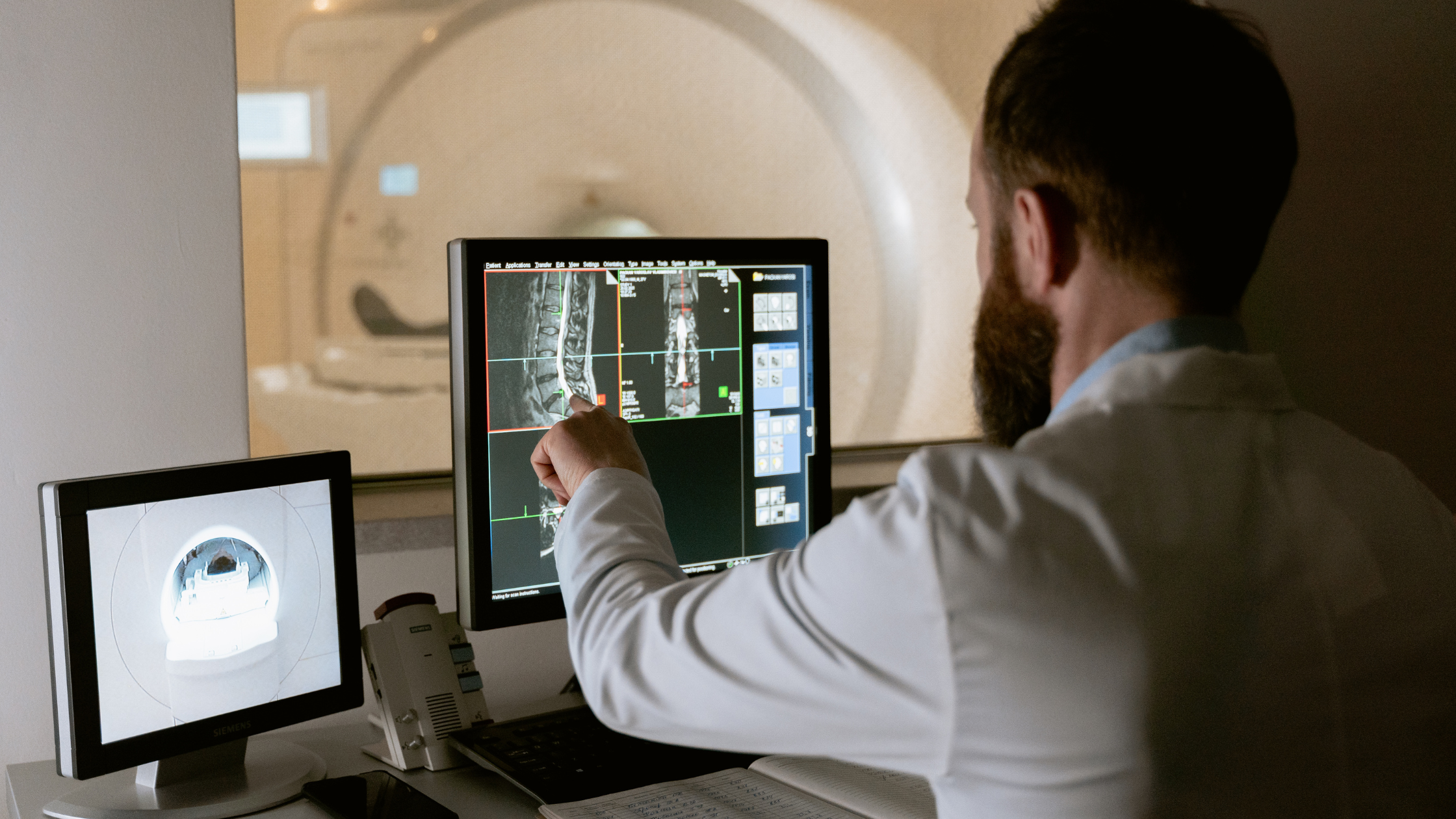
Medical technology has seen significant advancements, providing healthcare professionals with essential tools for accurate diagnoses. Among these tools, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has emerged as a crucial modality, particularly in assessing complex anatomical structures like the thyroid gland.
Understanding MRI:
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique utilizing a potent magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed, high-resolution images of the body's internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI doesn't employ ionizing radiation, ensuring its safety and versatility for examining different body parts.
Role of MRI in Thyroid Evaluation:
In diagnosing thyroid-related conditions, MRI plays a pivotal role, aiding medical professionals in various ways:
- Detailed Visualization: MRI offers highly detailed images of the thyroid and surrounding tissues, providing a comprehensive view of size, shape, and abnormalities such as nodules or tumors.
- Extension Assessment: It helps determine if thyroid conditions extend beyond the gland, visualizing potential invasion into nearby tissues or structures in the neck, which aids in staging and treatment planning.
- Vascular Assessment: MRI's imaging capability extends to visualizing blood vessels around the thyroid, aiding in assessing blood flow patterns and identifying vascular involvement related to thyroid disorders or tumors.
- Precise Preoperative Planning: For surgical intervention, MRI guides surgeons by providing detailed anatomical information and reducing risks by outlining the gland's relationship with adjacent structures.
- Tissue Differentiation: MRI distinguishes between various thyroid tissues, differentiating solid nodules, cysts, or abnormalities, aiding in determining the necessity for further investigations or biopsies.
- Monitoring Changes and Treatment Response: Over time, MRI tracks changes within the thyroid, evaluating treatment effectiveness and guiding ongoing management strategies.
Preparing for a Neck and Thyroid MRI:
Before the procedure:
- Discuss with your healthcare provider or imaging center for personalized instructions.
- Disclose your medical history, allergies, prior surgeries, and the presence of any implants or metal devices.
- Wear comfortable, metal-free clothing, and remove all metal accessories.
- Adhere to dietary restrictions or medication guidelines provided.
- Communicate any claustrophobia or anxiety concerns to receive appropriate support.
- Follow all instructions provided for a smooth and accurate MRI experience.
Choosing Imaging Techniques: MRI vs. Ultrasound
MRI:
- Provides detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves.
- Useful for soft tissue evaluation without radiation exposure.
- Suitable for comprehensive assessments but may require contrast agents.
Ultrasound:
- Uses sound waves for real-time imaging, particularly effective for thyroid evaluation.
- Non-invasive, painless, and cost-effective.
- Preferred for initial thyroid assessments due to its ability to detect nodules.
Selection between MRI and ultrasound depends on clinical requirements and the information sought by healthcare providers. Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable imaging modality based on your symptoms and medical history.
Conclusion:
MRI serves as an indispensable tool for assessing thyroid health. Its ability to provide detailed images, evaluate extensions, differentiate tissues, and assist in treatment planning highlights its pivotal role in the comprehensive understanding and management of thyroid-related conditions. The careful consideration of imaging modalities based on individual patient needs remains crucial for accurate diagnoses and effective treatment strategies.
FAQs
-
What does an MRI of the neck and thyroid entail?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) of the neck and thyroid is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure utilizing magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the neck area, including the thyroid gland, nearby tissues, blood vessels, and nerves.
-
Why might a healthcare provider suggest an MRI of the neck and thyroid?
Healthcare providers recommend an MRI to assess various thyroid conditions, such as identifying nodules, and tumors, evaluating thyroid size and shape, determining the extent of abnormalities, and examining adjacent structures for potential involvement.
-
How is an MRI of the neck and thyroid performed?
During the procedure, individuals lie on a table that slides into the MRI machine. The machine generates detailed images without employing ionizing radiation. Patients need to remain still for clear image acquisition.
-
Is an MRI of the neck and thyroid safe?
Yes, an MRI is considered safe as it doesn't involve radiation exposure. However, individuals with specific metallic implants or devices should inform their healthcare provider beforehand, as these objects might interfere with the MRI.
-
Are there specific preparations needed before an MRI of the neck and thyroid?
Generally, there are no dietary restrictions before an MRI. However, patients may need to remove metal accessories or inform the healthcare provider about any metal implants or devices. Following personalized instructions from the healthcare provider or imaging center is essential.
-
What is the typical duration of an MRI of the neck and thyroid?
The duration of the MRI scan varies but usually lasts between 30 to 60 minutes. Timing may vary depending on specific imaging needs or if contrast dye is used.
-
Can normal activities be resumed immediately after an MRI of the neck and thyroid?
Yes, most individuals can resume regular activities right after an MRI, unless advised otherwise by the healthcare provider.
-
Will the results be available immediately after the MRI?
Generally, the MRI images are interpreted by a radiologist, and the results are provided to the healthcare provider who ordered the scan. The time to receive results may vary depending on the facility's procedures.