Head and Neck Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Prevention
Head and neck cancer includes various types of cancer that start in the mouth, throat, voice box, nose, and salivary glands. This cancer type can be very harmful, but detecting it early and taking preventive measures can significantly improve the chances of recovery. This detailed guide offers the latest information on the signs, diagnosis, and prevention of head and neck cancer.
Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancer
Early detection of head and neck cancer symptoms is crucial for prompt treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Persistent Sore Throat A sore throat that doesn't improve with time or treatment could indicate the presence of cancerous cells in the throat or nearby regions.
- Unexplained Weight Loss Sudden and unintentional weight loss can signify various cancers, including head and neck.
- Swelling or Lump: A lump or swelling in the neck, jaw, or mouth that persists for more than two weeks should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Voice Changes Hoarseness or other changes in the voice, mainly if they last more than two weeks, can be a symptom of laryngeal cancer.
- Difficulty Swallowing Pain or difficulty when swallowing may indicate cancer in the pharynx or esophagus.
- Ear Pain Persistent ear pain, wildly unrelated to an ear infection, can be associated with throat cancer.
- Nasal Obstruction or Bleeding Chronic nasal congestion or frequent nosebleeds can be symptoms of cancer in the nasal cavity or sinuses.
What Causes Cancers of the Head and Neck and Who's at Risk?
Understanding the causes and risk factors for head and neck cancer is crucial for prevention. Several factors contribute to the development of these cancers:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection A recent review of studies reveals that HPV infection accounts for 73% of head and neck cancers in the United States, primarily affecting the oropharynx, including the base of the tongue and tonsils.
- Tobacco Use Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as using smokeless tobacco, significantly increases the risk of head and neck cancers. Tobacco use is a primary risk factor for cancers of the oral cavity, larynx, and pharynx.
- Alcohol Consumption Heavy and prolonged alcohol use is a significant risk factor. Alcohol, particularly when combined with tobacco use, dramatically increases the likelihood of developing head and neck cancers.
- Poor Oral Hygiene Inadequate oral hygiene and dental care can contribute to the risk of cancers in the oral cavity and pharynx.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals, such as asbestos, wood dust, and synthetic fibers, can increase the risk of cancers of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
- Radiation Exposure Previous radiation treatment to the head or neck area for other medical conditions can increase the risk of developing cancer in these regions.
- Diet and Nutrition A diet low in fruits and vegetables is associated with a higher risk of head and neck cancers. Nutritional deficiencies can weaken the body's defenses against cancer.
- Genetic Predisposition A family history of head and neck cancer can indicate a genetic susceptibility, putting individuals at higher risk.
Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer
Early and accurate diagnosis proves crucial for effective treatment. The following methods commonly diagnose head and neck cancer:
- Physical Examination: A thorough head and neck examination can reveal lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities.
- Endoscopy An endoscope allows doctors to view the inside of the nasal passages, throat, and larynx to detect abnormal growths.
- Biopsy In a biopsy, a medical professional takes a small tissue sample from a suspicious area to examine it under a microscope for cancer cells.
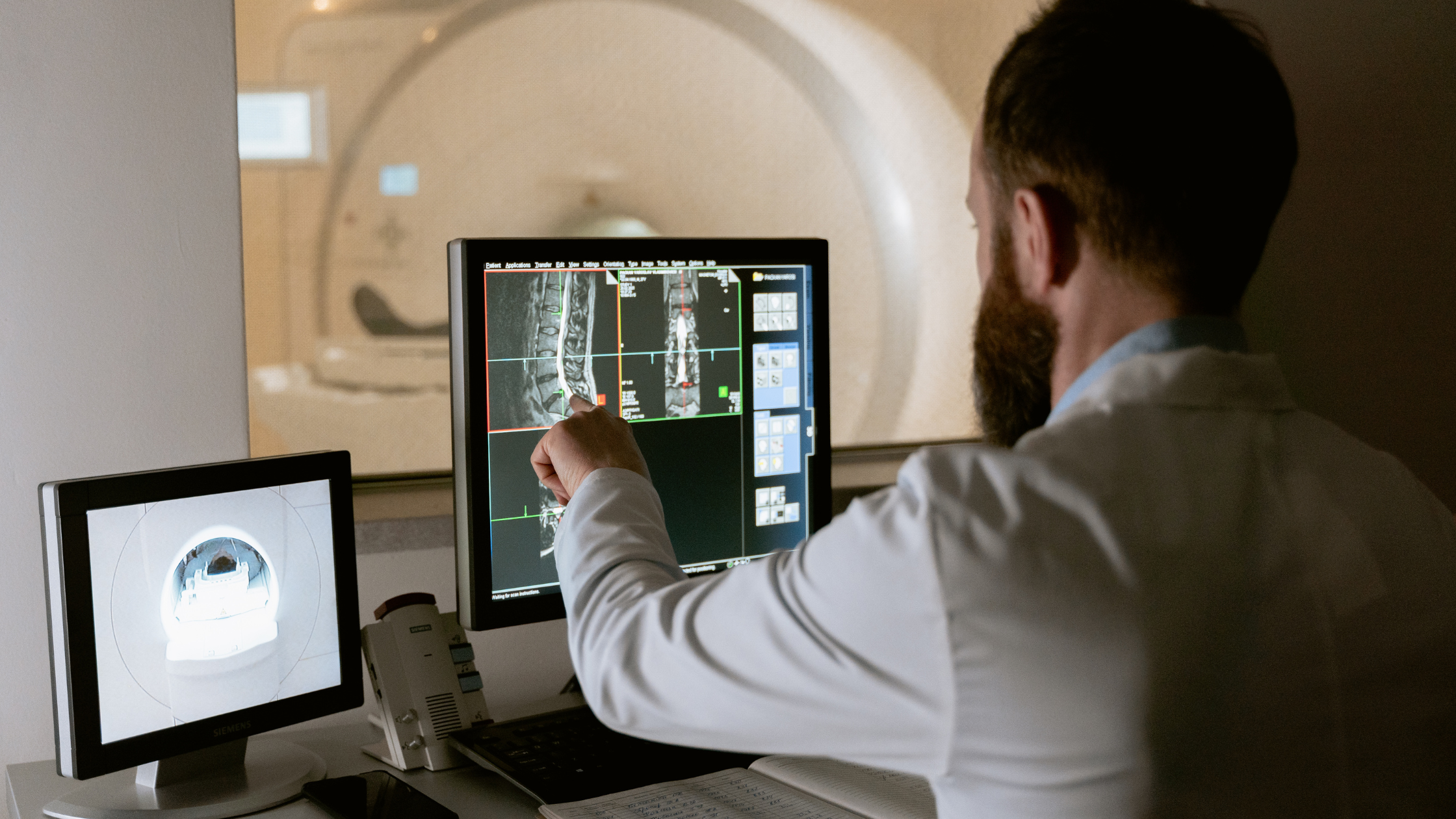
- Imaging Tests CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans provide detailed images that help identify the location and extent of the cancer.
- Blood Tests While blood tests alone cannot diagnose head and neck cancer, they can provide information about a patient's overall health and detect markers that suggest the presence of cancer.
Prevention of Head and Neck Cancer
Preventing head and neck cancer involves lifestyle changes and regular medical checkups. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
- Avoid Tobacco Use
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene
- Protect Against HPV
- Healthy Diet
- Regular Medical Checkups
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of head and neck cancer is vital for successful treatment. Many symptoms of head and neck cancer can be mistaken for other less severe conditions, which often leads to delays in diagnosis. Regular checkups and being aware of the symptoms can help catch cancer early.
Treatment Options for Head and Neck Cancer
Treatment for head and neck cancer depends on the cancer's location, stage, and the patient's overall health. Common treatments include:
- Surgery Surgical procedures aim to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving as much function as possible.
- Radiation Therapy utilizes high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells, often combined with surgery or chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It can be administered alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs targeting cancer cells without harming normal cells.
- Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. It is a newer approach and can be effective for some patients.
Support and Resources
Living with head and neck cancer can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to help patients and their families. Support groups, counseling, and educational resources can provide emotional and practical support throughout treatment.