Decoding Health: What Brain Scans Reveal About Your Vitality
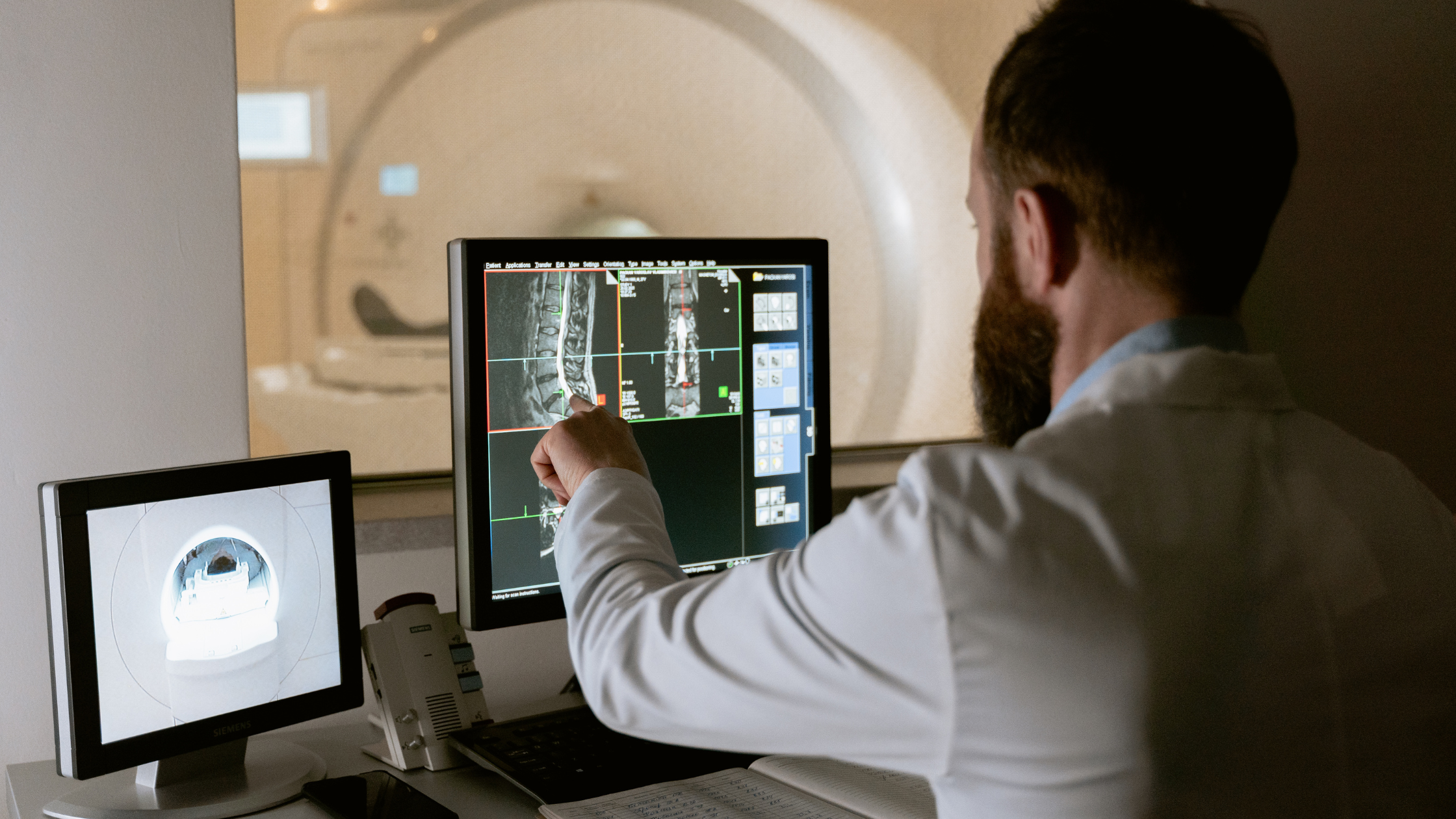
Brain scans, a powerful diagnostic tool, have traditionally been associated with neurological conditions. However, they are now revealing a wealth of information about a person's overall health and well-being.
In this article, we will explore how a brain scan can provide insights into various aspects of your health, from mental conditions to cardiovascular health, and much more.
The Multifaceted Nature of Brain Scans
Brain scans are a diverse range of diagnostic imaging techniques that provide detailed images of the brain's structure and function. They have revolutionized our understanding of the human brain and its various intricacies.
The most common types of brain scans include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT) scans, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, and functional MRI (fMRI). Here's a brief overview of the differences between them:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- Principle: Uses magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body's internal structures.
- Applications: It is versatile and commonly used to visualize the brain, spinal cord, joints, muscles, and soft tissues. MRI is excellent for detecting tumors, assessing structural abnormalities, and providing information about blood flow.
CT (Computed Tomography):
- Principle: It involves X-rays and a computer in creating cross-sectional images (slices) of the body, which are then compiled to form a 3D image. Applications: Widely used for imaging bones, the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. CT scans are valuable for identifying fractures, tumors, and various conditions. It's especially good for rapidly imaging trauma cases.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography):
- Principle: It utilizes a small amount of radioactive material (radiotracer) that medical professionals inject into the body. The PET scanner detects gamma rays emitted by the radiotracer, which provides information about the body's metabolic activity.
- Applications: Primarily used to study cellular functions and metabolism. Medical professionals often use PET in oncology to identify and stage tumors, and in neurology for studying brain function.
fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- Principle: A specialized form of MRI that measures changes in blood flow and oxygenation in the brain, which are associated with neural activity.
- Applications: Primarily used in neuroscience and psychology to study brain function. It can help researchers and clinicians understand brain activity during various tasks and identify regions associated with specific functions or disorders.
Mental Health Insights
Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia can leave a profound impact on the brain's structure and function. Brain scans can detect these changes, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Neurodegenerative diseases
Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative conditions often manifest as specific brain abnormalities. Advanced brain imaging can help in the early detection of these diseases, allowing for more effective intervention and management.
Cognitive Decline and Dementia
As we age, cognitive decline becomes a concern. Brain scans can help differentiate normal age-related changes from more serious conditions like dementia, aiding in early intervention and planning.
Substance Abuse Effects
The impact of substance abuse on the brain is well-documented. Brain scans can reveal the damage caused by drugs and alcohol, influencing treatment decisions and motivating individuals to seek help.
Detecting Brain Tumors
Brain scans are crucial in the early detection of brain tumors. Whether benign or malignant, these growths can cause a range of symptoms and must be treated promptly. Brain scans not only identify the presence of tumors but also help in surgical planning.
Traumatic Brain Injuries
Concussions and other traumatic brain injuries can have long-lasting effects. Brain scans are essential for assessing the extent of damage, guiding treatment, and predicting recovery outcomes.
Stroke Risk Assessment
Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide. Certain brain scan techniques can reveal the presence of arterial blockages and aneurysms, helping doctors assess an individual's stroke risk.
Cardiovascular Health
An unhealthy heart can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain, which can result in cognitive decline and an increased risk of strokes. Brain scans can reveal the impact of cardiovascular conditions on brain tissue.
Hormonal and Metabolic Influences
Your hormones and metabolism play a significant role in brain health. Conditions like diabetes and thyroid disorders can impact brain function. Brain scans can show how these conditions affect the brain and guide treatment strategies.
Personalized Medicine
In the era of personalized medicine, brain scans are playing an increasingly important role. They allow doctors to tailor treatments to an individual's specific brain structure and function, maximizing the chances of successful outcomes.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
For many health conditions, especially neurological and psychiatric disorders, it's crucial to monitor the progress of treatment. Brain scans provide a quantitative way to track changes in the brain over time, helping doctors assess the effectiveness of interventions.
Ethical Considerations
While brain scans offer tremendous benefits, they also raise ethical concerns, especially in terms of privacy and consent. Patients must be well-informed about the implications of brain scans and their potential use in healthcare decision-making.
Conclusion: Your Brain, Your Health
In conclusion, a brain scan is not just a diagnostic tool for neurological conditions; it's a window into your overall health. From mental health and neurodegenerative diseases to cardiovascular health and substance abuse effects, brain scans provide insights that can lead to early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
As the field of medical imaging continues to advance, we can expect even more breakthroughs in our ability to use brain scans to reveal the secrets of health, helping individuals lead better and longer lives.
FAQs
1. What is a Brain MRI with Contrast?
During a Brain MRI with contrast, medical professionals inject a contrast agent, usually a gadolinium-based dye, into the patient's bloodstream before conducting the MRI scan. This contrast agent enhances the visibility of specific areas of the brain, blood vessels, or abnormalities, thereby making them more discernible in the resulting MRI images.
2. What is the Difference Between a Head MRI and a Brain MRI?
Medical professionals often use a Head MRI and a Brain MRI interchangeably, although there exists a subtle difference between them. A Head MRI typically includes images of the entire head, which may also cover the skull, face, and neck, in addition to the brain. In contrast, a Brain MRI specifically focuses on the brain and its internal structures.
3. What Does a Brain MRI Show?
A Brain MRI can reveal a wide range of information, including brain structure, abnormalities, injuries, tumors, blood flow, and other functional aspects. It is a valuable tool for diagnosing conditions like tumors, strokes, neurological disorders, and assessing overall brain health.
4. What Is the Difference Between MRI with and without Contrast?
The primary difference between an MRI with and without contrast lies in the use of a contrast agent. MRI with contrast involves the injection of a contrast dye into the bloodstream to enhance the visibility of specific structures or abnormalities. MRI without contrast relies solely on the magnetic field and radio waves to create images without the use of contrast agents.